Article
소석회와 에탄올 혼합물의 닭진드기에 대한 살비 효과
홍의철1,†,*
,
박기태2,*
,
강보석1
,
강환구1
,
전진주1
,
김현수1
,
손지선1
,
김찬호3
Acaricidal Effect of Mixtures of Hydrated Lime and Ethanol on Poultry Red Mite (Dermanyssus gallinae)
Euichul Hong1,†,*
,
Ki-Tae Park2,*
,
Bo-Seok Kang1
,
Hwan-Ku Kang1
,
Jin-Joo Jeon1
,
Hyun-Soo Kim1
,
Jiseon Son1
,
Chan-Ho Kim3
Author Information & Copyright ▼
2경기도경제과학진흥원 바이오센터 효능평가팀 책임연구원
1Researcher, Poultry Research Institute, National Institute of Animal Science, Pyeongchang 25342, Republic of Korea
2Senior Researcher, Gyeonggido Business & Science Accelerator, Suwon 16229, Republic of Korea
3Postdoctoral Researcher, Poultry Research Institute, National Institute of Animal Science, Pyeongchang 25342, Republic of Korea
* These authors have contributed equally to this work.
© Copyright 2019, Korean Society of Poultry Science. This is an Open-Access article distributed under the terms of the
Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits
unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any
medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Received: Jan 04, 2020; Revised: Feb 14, 2020; Accepted: Feb 17, 2020
Published Online: Mar 31, 2020
적 요
본 연구는 닭진드기에 대한 소석회와 에탄올의 살비 효과를 구명하기 위하여 세 가지 시험을 수행하였다. 첫 번째 시험 처리구는 소석회 무처리를 대조구로 하고, 소석회 10%와 20% 수용액을 각각의 처리구로 하였다. 두 번째 시험 처리구는 총 8처리구로 에탄올을 30%, 40%, 50%, 60%, 70%, 80%, 90%, 100%로 희석하여 각각의 처리구로 하였다. 세 번째 시험 처리구는 소석회 2수준(10%, 20%)와 에탄올 3수준(30%, 40%, 50%)을 혼합하여 2 × 3의 총 6처리구로 하였다. 모든 처리구는 처리구당 3반복씩 시험을 수행하였다. 첫 번째 시험에서는 10%와 20% 소석회 수용액 처리 시 닭진드기의 살비율은 각각 74.0%와 92.3%로 나타났으며(P<0.05). 대조구의 살비율은 0%로 나타났다. 두 번째 시험에서는 30% 에탄올 희석액에서 1.67%로 가장 낮았고, 40% 희석액에서 8.33%, 50% 희석액에서 7.47%로 차이가 없었으며, 60%와 70% 희석액은 각각 42.4%와 84.7%로 나타났고, 80% 이상의 희석액에서는 100%의 살비율이 관찰되었다(P<0.05). 세 번째 시험에서는 소석회+에탄올 혼합물에 의한 닭진드기의 살비 효과는 모든 처리구에서 100%로 관찰되었다. 결론적으로, 경제성 및 안전성을 고려하여 10% 소석회 수용액과 30% 에탄올의 혼합물이 닭진드기 방제 후보물질로서 적합하다고 판단된다.
ABSTRACT
This study intended to investigate the effects of slaked lime and ethanol on poultry red mites (PRM) in the coops of laying hen. Three experiments were conducted to this effect. The first used untreated hydrated lime as a control and 10% and 20% aqueous solutions of hydrated lime were used as treatments. The second experiment used 30%, 40%, 50%, 60%, 70%, 80%, 90%, and 100% ethanol solutions as treatments. The third experiment used hydrated lime in two distinct concentrations (10% and 20%) and 30%, 40%, and 50% ethanol solutions mixed to yield a total of 6 (2 × 3) treatments. All treatments were tested three times each. In the first experiment, the PRM killing rates were 74.0% and 92.3% when treated with 10% and 20% hydrated lime solutions, respectively. The acaricidal activity of the control sample was 0%. In the second experiment, the lowest value was 1.67% for the 30% ethanol solution, 8.33% for the 40% solution, and 7.47% for the 50% solution. The acaricidal activities of the 60% and 70% solutions were 42.4% and 84.7%, respectively. A 100% acaricidal activity was observed in dilutions above 80% (P<0.05). In the third experiment, the PRM killing effect of the hydrated lime + ethanol mixture was 100% in all treatments. In conclusion, after taking into consideration the economical and safety factors, a mixture of 10% hydrated lime solution and 30% ethanol is considered to be a suitable candidate for controlling PRM.
Keywords: 산란계; 닭진드기; 소석회; 에탄올; 방제
Keywords: laying hen; poultry red mite; hydrated lime; ethanol; control
서 론
닭진드기는 전 세계적으로 흡혈을 통해 산란계에 직접 피해를 주는 대표적 외부기생충으로 알려져 있다(Höglund et al., 1995). 많은 산란계 농가가 사육 방식에 관계없이 닭진드기에 감염된 것으로 보고되고 있으며, 특히 EU(약 83%, Flochlay et al., 2017), 일본(약 85%, Bartley 등, 2017)에서는 산란계 농가의 감염률이 높은 것으로 추정되고 있다. 국내에서는 가금수의학회에서 2017년에 120개의 산란계 농장에서 감염률을 조사한 결과, 약 94% 정도가 닭진드기에 감염이 된 것으로 확인되었다. 닭진드기로 인한 첫 번째 피해는 흡혈로 인한 스트레스를 들 수가 있으며, 이는 심한 경우 폐사까지 일으킬 수 있다(George et al., 2015). 또한, 산란율을 저하시키면서 세균 및 바이러스성 질병을 전파하는 위험이 있으며(Moro et al., 2005, 2007), 농장 관리자에게 옮겼을 때 소양증 및 알레르기성 피부염 등을 야기할 수 있다(Abjigoudarzi et al., 2013). 닭진드기는 5~45°C의 온도 조건에서 생존이 가능하고, 흡혈을 하지 않아도 9개월까지 살아남을 수 있으며, 번식력이 왕성하여 퇴치가 어렵다(Nordenfors et al., 1999). 닭진드기는 어둡고 따뜻하고 습한 곳을 좋아하는 습성이 있으며, 낮에는 케이지 안쪽, 사료통 안쪽, 에어덕트 내부 등 방제가 어려운 계사 구석에 군집을 이루며 숨어있다가 밤이 되면 닭에게 가서 흡혈을 한다(Wang 등, 2019).
많은 국가에서 닭진드기 방제를 위해 농약 잔류 위험이 없는 천연 살비제의 효력 검증 및 보급에 많은 노력을 기울이고 있다. Essential oil, silica 및 식물추출물에 대하여 닭진드기 제어 효력과 관련된 많은 실험들이 있었으며(Maurer et al., 2009; George et al., 2010; Magdaş.et al., 2010), 일부 외국에서는 소석회를 이용한 살모넬라 등의 유해 미생물 증식 억제 효과를 평가한 사례가 있었다(Alam et al., 2018). 또한, 육계사의 딱정벌레(외미거저리)에 의한 살충 효과가 보고되었으며(Wolf et al., 2015), 항균용 소독제로써 70% 에탄올의 효과도 알려져 있다(Ribeiro et al., 2015). 그러나 이런 물질들의 닭진드기 제어 효력에 대한 직접적인 실험결과는 없는 상황이다. 따라서 본 실험에서는 농약 잔류 위험이 없는 천연 살비후보물질로써 소석회와 에탄올 혼합물에 대한 닭진드기 살비 효력을 평가하였다.
재료 및 방법
1. 닭진드기 채집
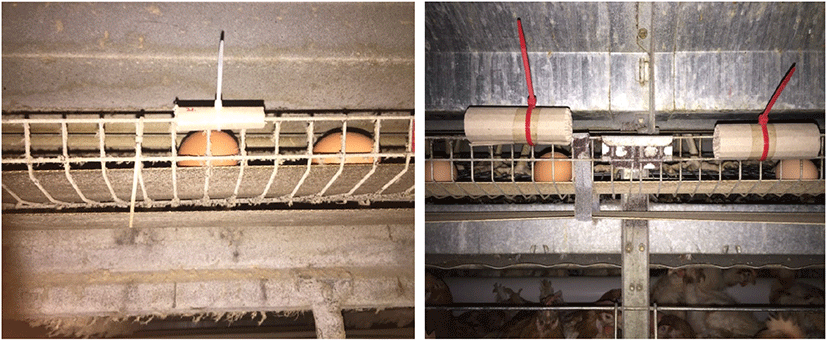
닭진드기는 경기도 안성시 및 여주시 소재 산란계 농장에서 포획장치를 활용하여 대량 채집하였다. 포획장치는 시중에서 쉽게 구할 수 있는 골판지를 5 × 6 cm와 10 × 30 cm 로 잘라 말아준 후 계사 내 계란 받이 앞에 부착하였고, 2일 후 수거하여 10일 안에 시험을 수행하였다(Fig. 1).
2. 시험설계
본 시험에 사용된 소독제는 소석회(95% calcium hydroxide, Samchun chemical, Korea)와 에탄올(99.5% Ethyl alcohol anhydrous(Daejung chemical, Korea)), 그리고 이들의 혼합물을 사용하여 세 가지 시험을 수행하였다(Table 1).
<시험 1>은 소석회를 단독 사용시에 진드기 사멸 효과를 조사하였다. 처리구는 소석회 무처리를 대조구로 하고, 소석회 10%와 20% 수용액을 각각의 처리구로 하였다.
<시험 2>는 에탄올을 단독 사용시에 진드기 사멸 효과를 조사하였다. 처리구는 총 8처리구로 에탄올을 30%, 40%, 50%, 60%, 70%, 80%, 90%, 100%로 희석하여 각각의 처리구로 하였다.
<시험 3>은 소석회 2수준(10%, 20%)와 에탄올 3수준(30%, 40%, 50%)을 혼합하여 2 × 3의 총 6처리구로 하였다.
모든 처리구는 처리구당 3반복씩 시험을 수행하였다.
3. 닭진드기 살비효과 조사
포획한 닭진드기는 10일 이내의 것을 사용하였다. 50 × 15 mm의 페트리디쉬(Insect breeding dish, SPL Life Science, Korea)에 멸균된 여과지(Filter paper, Hyundai Micro Co., Korea)를 장착한 후 희석 배수 별로 준비된 시험물질을 분주하였다. 분주량은 시험물질마다 여과지를 통해 확산되는 정도가 각각 다르기 때문에 차별을 하여 분주하였다. 소석회 수용액 및 소석회+에탄올 혼합물의 경우, 여과지를 통해 물질이 확산이 잘 되지 않기 때문에, 여과지 전체에 골고루 접촉될 수 있는 최소 용량인 600 μL(1 mL 분주 후 여과지에 골고루 접촉되는 것 확인 후 400 μL 수거)를 분주하였고, 에탄올 희석액의 경우, 분주 시 여과지에 충분히 확산이 되기 때문에 최소 용량 150 μL를 분주하였다. 시험물질 분주 직후, 작은 붓을 이용하여 페트리디쉬에 닭진드기 성충을 접종하고, 24시간 후 닭진드기 성충의 사멸 수를 측정하였다. 사멸 닭진드기는 가는 붓을 이용하여 건드렸을 때, 움직임이 없는 개체로 간주하였다(Fig. 2).
4. 통계처리
본 시험에서 얻어진 모든 자료는 SAS(2012)의 GLM (Generation Linear Model) Program(one-way ANOVA procedure)을 이용하여 분석하였으며, 각 처리구 간의 평균값을 Duncan(Duncan, 1955)의 다중 검정을 이용하여 95% 신뢰수준에서 검정하였다.
Table 1.
Dilution ratio of disinfectants to control of poultry red mite
| Disinfectants |
Calcium hydroxide |
Ethanol (99.5%). |
Distilled water |
Total |
| ---------- (%) ---------- |
| Hydrated lime |
10 |
- |
90 |
100 |
| 20 |
- |
80 |
100 |
| Ethanol (99.5%) |
- |
30 |
70 |
100 |
| - |
40 |
60 |
100 |
| - |
50 |
50 |
100 |
| - |
60 |
40 |
100 |
| - |
70 |
30 |
100 |
| - |
80 |
20 |
100 |
| - |
90 |
10 |
100 |
| Hydrated lime + Ethanol (99.5%) |
10 |
30 |
60 |
100 |
| 10 |
40 |
50 |
100 |
| 10 |
50 |
40 |
100 |
| 20 |
30 |
50 |
100 |
| 20 |
40 |
40 |
100 |
| 20 |
50 |
30 |
100 |
Download Excel Table
Fig. 2.
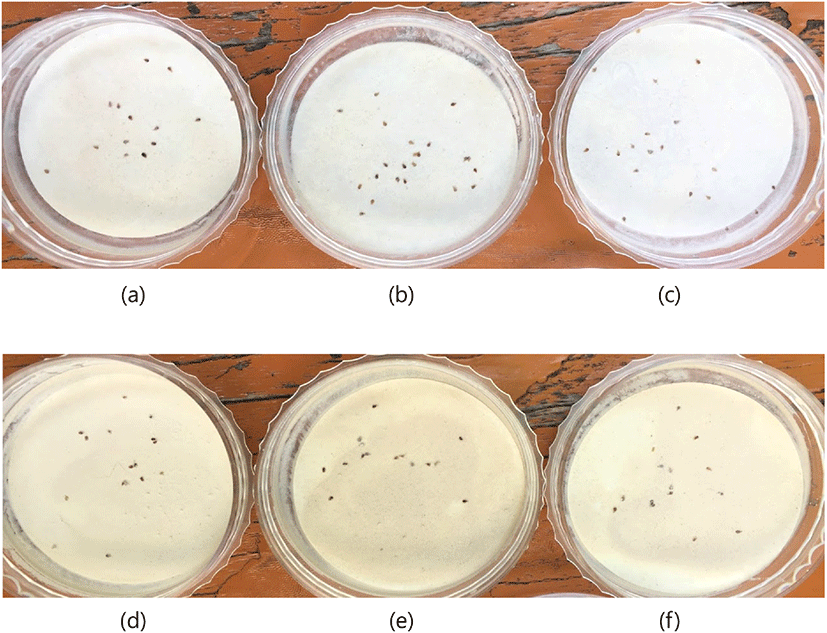
Dead mites by treating the mixture of calcium hydroxide and ethanol (a, 10% hydrated lime + 30% ethanol; b, 10% hydrated lime + 40% ethanol; c, 10% hydrated lime + 50% ethanol; d, 20% hydrated lime + 30% ethanol; e, 20% hydrated lime + 40% ethanol; f, 20% hydrated lime + 50% ethanol).
Download Original Figure
결 과
1. 소독제에 따른 닭진드기 살비효과
본 시험에서 소석회 수용액에 의한 닭진드기 살비 효력은 Table 2에 나타내었다. 시험결과 10%와 20% 소석회 수용액 처리 시 닭진드기의 살비율은 각각 74.0%와 92.3%로 나타났으며, 유의적인 차이가 있었다(P<0.05). 그러나 대조구에서는 0%의 살비 효력이 관찰되었다.
에탄올 희석액에 의한 닭진드기 살비 효력은 Table 3에 나타내었다. 실험결과, 30% 희석액에서 1.69%로 가장 낮았고, 40% 희석액에서 8.48%, 50% 희석액에서 7.14%로 차이가 없었으며, 60%와 70% 희석액은 각각 42.2%와 86.3%로 나타났고, 80% 이상의 희석액에서는 100%의 살비율이 관찰되었다(P<0.05).
소석회+에탄올 혼합물에 의한 닭진드기 살비 효과는 Table 4와 Fig. 2에 나타내었다. 모든 처리구에서 100%의 닭진드기 살비 효력이 관찰되었다.
고 찰
본 시험은 산란계 농장 내 닭진드기 방제를 위한 살충제 위험 없는 친환경적인 물질을 찾아내며, 물질의 효력을 과학적으로 증명하고자 수행하였다. 소석회와 에탄올의 유해 미생물 등에서의 소독 효과는 다수의 사례에서 찾아볼 수 있다(Plachy et al., 1996; Ribeiro et al., 2015; Alam et al., 2018; Kampf et al., 2018). 또한, 소석회의 경우 외미거저리에 대한 살충효과가 보고된 바 있으며(Wolf et al., 2015), 일부 국내 농장에서는 생석회를 이용한 닭진드기를 예방하고 있다고 알려져 있다. 하지만 생석회의 경우 물과 반응하여 200°C 정도의 열을 발산한 후 소석회로 변하게 되기 때문에 본 시험에서는 열로 인한 위험이 없는 소석회를 사용하였다. 소석회는 강알칼리(pH 12.5)를 띄고 있는 물질이며, 항균 작용에 의한 기전으로써 물과 반응했을 때, 세균의 세포막 및 DNA 손상, 단백질 변성을 일으킨다고 알려져 있다(Mohammadi et al., 2012). 에탄올의 경우 70%의 농도에서 항균용 소독제로 널리 사용되고 있으나(Ribeiro et al., 2015; Kampf, 2018), 닭진드기에 대한 에탄올의 효과를 조사한 연구는 전무한 실정이다.
Table 2.
Acaricidal effect of treating calcium hydroxide on the red mite of laying hens
| Treatments |
Number of mites |
Acaricidal effect (%) |
| Total |
Dead |
| Control (−) |
56 |
0 |
− |
| Hydrated lime |
10% |
54 |
40 |
74.1b |
| 20% |
52 |
48 |
92.4a |
| SEM1 |
4.35 |
| P-value |
<0.05 |
Download Excel Table
Table 3.
Acaricidal effect of treating ethanol on the red mite of laying hens
| Treatments |
Number of mites |
Acaricidal effect (%) |
| Total |
Dead |
| Ethanol (99.5%) |
30% |
59 |
1 |
1.69d |
| 40% |
59 |
5 |
8.48d |
| 50% |
56 |
4 |
7.14d |
| 60% |
64 |
27 |
42.2c |
| 70% |
73 |
63 |
86.3b |
| 80% |
64 |
64 |
100.0a |
| 90% |
63 |
63 |
100.0a |
| 100% |
68 |
68 |
100.0a |
| SEM1 |
7.09 |
| P-value |
<0.05 |
Download Excel Table
Table 4.
Acaricidal effect of treating mixtures (calcium hydroxide + ethanol) on the red mite of laying hens
| Treatments |
Number of mites |
Acaricidal effect (%) |
| Total |
Dead |
| 10% hydrated lime + 30% ethanol |
51 |
51 |
100.0 |
| 10% hydrated lime + 40% ethanol |
62 |
62 |
100.0 |
| 10% hydrated lime + 50% ethanol |
53 |
53 |
100.0 |
| 20% hydrated lime + 30% ethanol |
50 |
50 |
100.0 |
| 20% hydrated lime + 40% ethanol |
51 |
51 |
100.0 |
| 20% hydrated lime + 50% ethanol |
51 |
51 |
100.0 |
| SEM1 |
|
|
- |
| P-value |
|
|
- |
Download Excel Table
고 찰
본 시험에서는 먼저 소석회 수용액과 에탄올 희석액에 대한 각각의 효력을 우선 판단하였다. 소석회 수용액의 경우, 10% 소석회 수용액에서 74.0%, 20% 소석회 수용액에서 92.3%의 살비 효력이 관찰되었으나, 전체 닭진드기를 사멸시키지는 못하였다. 에탄올은 빠르게 증발하는 특성이 있음으로 희석액 투여 직후 닭진드기를 접종하여 살비 효력을 관찰하였다. 결과적으로 30~60%의 에탄올 단독 사용시에는 닭진드기 살비 효력이 인정되지 않았으며, 70% 이상의 에탄올 농도에서 80% 이상의 닭진드기 살비 효력이 관찰되었고, 80% 이상의 에탄올에서는 100%의 살비 효력이 관찰되었다.
소석회 수용액에 에탄올을 혼합하였을 때, 닭진드기를 100% 사멸시키는 것이 확인되었다. 또한, 30~50%의 에탄올 자체만으로는 효력이 보이지 않았으나, 소석회 수용액이 혼합됨으로써 닭진드기를 완전 사멸시키게 되었는데, 이는 빠르게 증발하는 에탄올을 소석회 수용액이 억제하여 에탄올의 유효성분이 닭진드기에 접촉됨으로써 두 물질의 상승작용이 일어났음으로 사료된다. 그러나 어떤 원리에 의해 살비 효과가 발생하는지는 본 연구에서는 이뤄지지 않았으며, 이에 대한 과학적인 원리를 증명하기 위해 추후 추가적인 실증 시험이 필요할 것으로 판단된다.
결론적으로, 본 시험에서 경제성 및 안전성을 고려하여 처리구 중 가장 적은 농도이며 100%의 사멸효과가 관찰된 10% 소석회 수용액과 30% 에탄올의 혼합물이 닭진드기 방제 후보물질로서 적합하다고 판단된다.
현재까지 닭진드기 방제를 위해 소석회 및 소석회와 에탄올의 혼합물을 직접 혹은 간접적으로 적용한 사례는 찾아볼 수 없다. 본 연구에서 사용된 소석회+에탄올 혼합물을 계군이 출하된 빈 계사에 도포한 경우, 닭진드기 밀도가 감소될 뿐만 아니라 그 효능이 장시간 지속될 것으로 추정된다.
따라서 이러한 혼합물의 추가적인 현장 내 검증 등을 통해 실질적으로 계사 내 닭진드기 밀도 억제에 도움을 줄 수 있을 뿐만 아니라, 국내 산란계 농가 생산성 향상 및 경쟁력 강화를 도모할 수 있으리라고 생각된다.
사 사
본 연구는 농촌진흥청 공동연구사업(과제번호: PJ01345501)에 의해 이루어진 것으로 이에 감사 드립니다.
REFERENCES
Abdigoudarzi M, Mirafzali MS, Belgheiszadeh H 2013 Human infestation with
Dermanyssus gallinae (Acari: Dermanyssidae) in a family referred with pruritus and skin lesions. J Arthropod Borne Dis 8(1):119-123.

Alam MS, Takahashi S, Ito M, Suzuki M, Komura M, Sangsriratanakul N, Shoham D, Takehara K 2018 Bactericidal efficacy of food additive–grade calcium hydroxide against
Salmonella infantis on eggshells. Avian Dis 62(2):177-183.

,


Bartley K, Turnbull F, Wright HW, Huntley JF, PalareaAlbaladejo J, Nath M, Nisbeta AJ 2017 Field evaluation of poultry red mite (
Dermanyssus gallinae) native and recombinant prototype vaccines. Vet Parasitology 244: 25-34.

,

,


George DR, Finn RD, Graham KM, Mul MF, Maurer V, Claire Moro CV, Sparagano OAE 2015 Should the poultry red mite
Dermanyssus gallinae be of wider concern for veterinary and medical science? Parasit Vectors 8(1):178-187.

,

,


George DR, Olatunji G, Guy JH, Sparagano OAE 2010 Effect of plant essential oils as acaricides against the poultry red mite,
Dermanyssus gallinae, with special focus on exposure time. Vet Parasitology 169:222-225.

,


Höglund J, Nordenfors H, Uggla A 1995 Prevalence of the poultry red mite,
Dermanyssus gallinae, in different types of production systems for egg layers in Sweden. Poult Sci 74(11):1793-1798.

,


Kampf G 2018 Efficacy of ethanol against viruses in hand disinfection. J Hosp Infect 98(4):331-338.

,

,


Magdaş C, Cernea M, Baciu H, şuteu E 2010. Acaricidal effect of eleven essential oils against the poultry red mite
Dermanyssus gallinae (Acari: Dermanyssidae). Sci Parasitol 11(2):71-75.

Maurer V, Perler E, Heckendorn F 2009
In vitro efficacies of oils, silicas and plant preparations against the poultry red mite
Dermanyssus gallinae. Exp Appl Acarol 48(1-2): 31-41.

,


Mohammadi Z, Shalavi S, Yazdizadeh M 2012 Antimicrobial activity of calcium hydroxide in endodontics: a review. Chonnam Med J 48(3):133-140.

,

,


Nordenfors H, Höglund J, Uggla A 1999 Effects of temperature and humidity on oviposition, molting, and longevity of
Dermanyssus gallinae (Acari: Dermanyssidae). J Medical Entomology 36(1):68-72.

,


Plachy P, Juris P 1996 Use of hydrated lime for disinfection of model pathogens Salmonella typhimurium and
Ascaris suum in sewage sludges. Vet Med (Praha) 41(8):255-259.

Ribeiro MM, Neumann VA, Padoveze MC, Graziano KU 2015 Efficacy and effectiveness of alcohol in the disinfection of semi-critical materials: a systematic review. Rev Latino-Am Enfermagem 23(4):741-752.

,

,


Sigognault Flochlay A, Thomas E, Sparagano O 2017 Poultry red mite (
Dermanyssus gallinae) infestation: a broad impact parasitological disease that still remains a significant challenge for the egg-laying industry in Europe. Parasit Vectors 10(1):357-362.

,

,


Valiente Moro C, Chauve C, Zenner L 2005 Vectorial role of some dermanyssoid mites (Acari, Mesostigmata, Dermanyssoidea). Parasite 12(2):99-109.

,


Valiente Moro C, Fravalo P, Amelot M, Chauve C, Zenner L, Salvat G 2007 Colonization and invasion in chicks experimentally infected with
Dermanyssus gallinae contaminated by
Salmonella enteritidis. Avian Pathol 36(4):307-311.

,


Wang C, Huang Y, Ma Y, Xu X, Wan Q, Li H, Yu H, Pan B 2019 First record of
Aspergillus oryzae as an entomopathogenic fungus against the poultry red mite
Dermanyssus gallinae. Vet Parasitology 271:57-63.

,


Wolf J, Potrich M, Lozano ER, Gouvea A, Pegorini CS 2015 Combined physical and chemical methods to control lesser mealworm beetles under laboratory conditions. Poult Sci 94(6):1145-1149.

,